 Forces can be described as a push or pull on an object. They can be due to phenomena such as gravity, magnetism, or anything that might cause a mass to accelerate.
Forces can be described as a push or pull on an object. They can be due to phenomena such as gravity, magnetism, or anything that might cause a mass to accelerate. force, in mechanics, any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of a body or to distort it. The concept of force is commonly explained in terms of Isaac Newton ’s three laws of motion set forth in his Principia Mathematica (1687).
force, in mechanics, any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of a body or to distort it. The concept of force is commonly explained in terms of Isaac Newton ’s three laws of motion set forth in his Principia Mathematica (1687).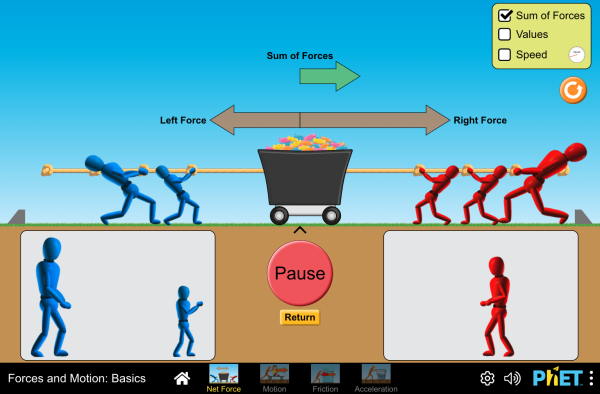 Explore the forces at work when pulling against a cart, and pushing a refrigerator, crate, or person. Create an applied force and see how it makes objects move. Change friction and see how it affects the motion of objects.
Explore the forces at work when pulling against a cart, and pushing a refrigerator, crate, or person. Create an applied force and see how it makes objects move. Change friction and see how it affects the motion of objects. Force is push or pull. Unbalanced forces make an object accelerate. Forces on an object are usually balanced: forces in one direction are equal to forces in the opposite direction: No acceleration. Example: The forces are in balance at the top of this bridge tower.
Force is push or pull. Unbalanced forces make an object accelerate. Forces on an object are usually balanced: forces in one direction are equal to forces in the opposite direction: No acceleration. Example: The forces are in balance at the top of this bridge tower.